2014/03/31
Lysine Methylation Mapping of Crenarchaeal DNA-Directed RNA Polymerases by Collision-Induced and Electron-Transfer Dissociation Mass Spectrometry
Enzymatic machineries fundamental for information processing (e.g. transcription, replication, translation) in Archaea are simplified versions of their eukaryotic counterparts. This is clearly noticeable in the conservation of sequence and structure of corresponding enzymes (see for example the archaeal DNA-directed RNA polymerase (RNAP)). In Eukarya, post translational modifications (PTMs) often serve as functional regulatory factors for various enzymes and complexes. Among the various PTMs, methylation and acetylation have been recently attracting most attention. Nevertheless, little is known about such PTMs in Archaea, and cross-methodological studies are scarce.
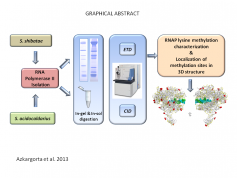
Post translational-modification analysis is always a challenging task. In this work, Dr. Mikel Azkargorta and Dr. Felix Elortza from the Proteomics Platform at CIC bioGUNE in collaboration with Dr. Nicola Abrescia's group examined methylation and N-terminal acetylation of endogenously purified crenarchaeal RNA polymerase from Sulfolobus shibatae (Ssh) and Sulfolobus acidocaldarius (Sac) by combining collision-induced dissociation (CID) and electron-transfer dissociation (ETD) mass spectrometry analysis. Overall, 20 and 26 methyl-lysines for S. shibatae and S. acidocaldarius were identified, respectively. Furthermore, two N-terminal acetylation sites for each of these organisms were assessed.
As a result, a high-confidence dataset for the mapping of methylation and acetylation sites in both Sulfolobus species has been reported, concluding that all observed methyl-lysines are mapped on the surface of the RNAP.
This study was recently published in Journal of Proteome Research:
Azkargorta M, Wojtas MN, Abrescia NG, Elortza F.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24625205
Figure legend: Strategy for Lysine methylation mapping of crenarchaeal DNA-directed RNA polymerases by collision-induced and electron-transfer dissociation mass spectrometry
See a large version of the first picture