2025/01/30
New therapeutic strategy to treat alcohol-related liver damage based on RNA therapeutics
A team led by Dr. Malu Martínez-Chantar, from CIC bioGUNE, has identified a new therapeutic target to treat alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD), focusing on the modulation of the magnesium transporter CNNM4.
The study, published in Hepatology and cover of this journal, proposes an innovative RNA interference-based strategy to reduce cellular damage and improve liver function.
This breakthrough offers new hope for addressing one of the leading causes of liver transplants worldwide.
An international research team led by Dr. Malu Martínez-Chantar, head of the Liver Disease Laboratory at CIC bioGUNE, member of BRTA, and researcher at CIBERehd, has identified a new therapeutic target that could revolutionize the treatment of alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD).
The study, of international scope, has been published in the prestigious journal Hepatology and selected for its cover. With Dr. Irene González Recio as the first author, it highlights an innovative approach based on the magnesium transporter CNNM4, which plays a key role in the development of this condition.
ALD is one of the leading causes of liver disease-related mortality worldwide. In Europe, it accounts for up to 80% of severe liver disease cases and is one of the primary reason for liver transplants in Western countries.
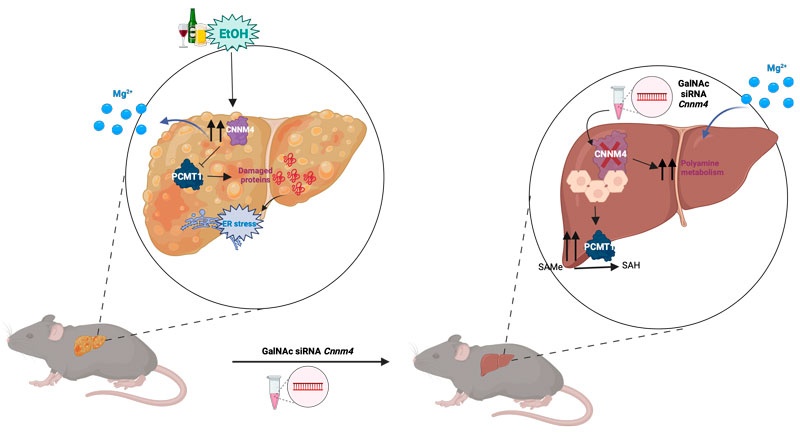
Magnesium is an essential cation for liver function, yet its deficiency is common in ALD patients and is associated with a more aggressive progression of the disease. The research reveals that the magnesium transporter CNNM4 is directly involved in the cation imbalance observed in patients and experimental models.
The researchers demonstrated that CNNM4 overexpression leads to magnesium imbalances that exacerbate cellular damage by affecting mitochondria and the system responsible for managing stress within liver cells. These disruptions are critical to understanding disease progression.
Furthermore, the study presents a pioneering approach using RNA molecules specifically designed to reduce CNNM4 activity in the liver. This technique, applied in experimental models, successfully restored cellular function, reduced liver damage, and improved SAMe levels, a compound essential for repairing proteins damaged by alcohol.
"Our discovery opens a completely new avenue for the treatment of alcohol-associated liver disease, providing a specific strategy based on RNA technology targeted to the liver," highlight Dr. Martínez-Chantar and Dr Gonzalez-Recio.
ALD encompasses various stages, from fat accumulation in the liver to severe alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. This discovery paves the way for new therapies that could significantly improve patients' quality of life.
Reference: Irene González-Recio, Naroa Goikoetxea-Usandizaga, Claudia M. Rejano-Gordillo, Carolina Conter, Rubén Rodríguez Agudo, Marina Serrano-Maciá, Leidy Estefanía Zapata-Pavas, Patricia Peña-Sanfélix, Mikel Azkargorta, Félix Elortza, José María Herranz, Álex Guillamon Thiery, Armando Raúl Guerra-Ruiz, Ramiro Jover, Unai Galicia-Garcia, César Martín, Ute Schaeper, Teresa C. Delgado, Irene Díaz-Moreno, Antonio Díaz Quintana, Daniela Buccella, Rubén Nogueiras, Josep Maria Argemi, Matías A. Ávila, Jordi Gratacós-Ginès, Paula Iruzubieta, Elisa Pose, Ramón Bataller, Javier Crespo, Luis Alfonso Martínez-Cruz, María Luz Martínez-Chantar. Modulatory effects of CNNM4 on protein-L-isoaspartyl-O-methyltransferase repair function during alcohol-induced hepatic damage. Hepatology. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001156.
About CIC bioGUNE
The Centre for Cooperative Research in Biosciences (CIC bioGUNE), member of the Basque Research & Technology Alliance (BRTA), located in the Bizkaia Technology Park, is a biomedical research organisation conducting cutting-edge research at the interface between structural, molecular and cell biology, with a particular focus on generating knowledge on the molecular bases of disease, for use in the development of new diagnostic methods and advanced therapies.
About BRTA
BRTA is an alliance of 4 collaborative research centres (CIC bioGUNE, CIC nanoGUNE, CIC biomaGUNE y CIC energiGUNE) and 13 technology centres (Azterlan, Azti, Ceit, Cidetec, Gaiker, Ideko, Ikerlan, Leartiker, Lortek, Neiker, Tecnalia, Tekniker y Vicomtech) with the main objective of developing advanced technological solutions for the Basque corporate fabric.
With the support of the Basque Government, the SPRI Group and the Provincial Councils of the three territories, the alliance seeks to promote collaboration between the research centres, strengthen the conditions to generate and transfer knowledge to companies, contributing to their competitiveness and outspreading the Basque scientific-technological capacity abroad.
BRTA has a workforce of 3,500 professionals, executes 22% of the Basque Country's R&D investment, registers an annual turnover of more than 300 million euros and generates 100 European and international patents per year.
See a large version of the first picture